Income Tax Slab for Financial Year 2024-25 & AY 2025-26 (New & Old Regime)
January 18, 2025 | by Morning Echoes

Income tax is a direct tax based on a progressive slab system, meaning the tax rate increases as the taxpayer’s income grows. Under the Income-tax Act, 1961, taxpayers can choose between two regimes:
- Old Regime – Offers various deductions and exemptions to reduce taxable income.
- New Regime – Features lower tax rates but does not allow exemptions or deductions.
This flexibility enables taxpayers to select the regime that best aligns with their financial goals.
Key Changes Introduced in Budget 2024:
- Revised Tax Slabs: Adjustments have been made to the tax slabs under the new regime.
- Increased Standard Deduction: Salaried employees can now claim a higher standard deduction of ₹75,000 under the new regime.
- Higher Deduction for Family Pension: The deduction for family pension has been increased from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000.
- Enhanced NPS Contribution Deduction: The deduction limit for the employer’s contribution to the National Pension System (NPS) has been raised from 10% to 14%.
Benefit to Salaried Employees:
With these changes, a salaried employee in the new tax regime can save up to ₹17,500 in taxes.
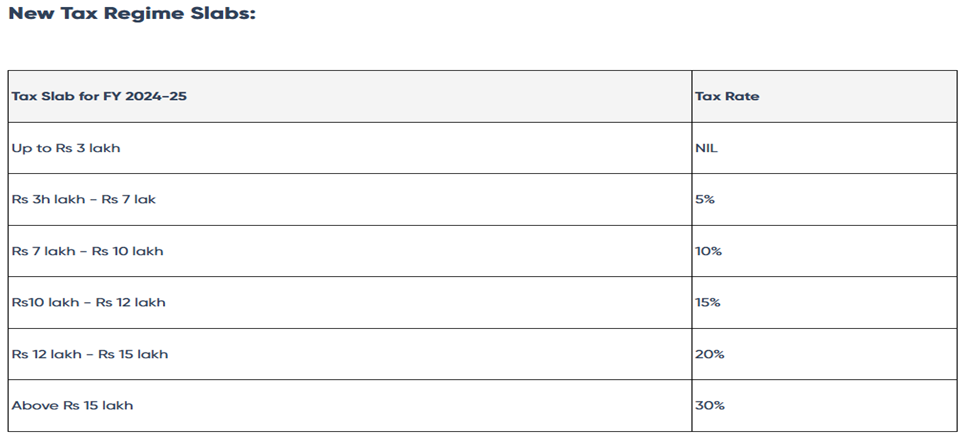

Revised New Tax Regime: Key Changes and Their Impact
The Union Budget 2024 has unveiled major updates to the income tax framework, focused on simplifying the system and providing greater relief to taxpayers. The revised tax slabs feature expanded thresholds, allowing more individuals to benefit from reduced tax rates. These updates highlight the government’s intent to enhance disposable income while encouraging wider adoption of the new tax regime.
Below is a summary of the changes introduced under the new regime for the benefit of taxpayers:
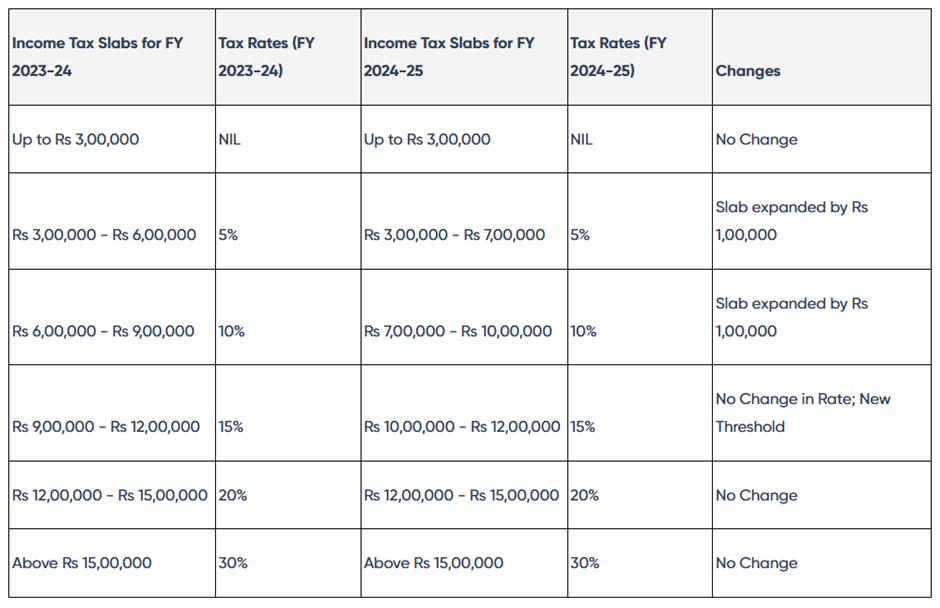
Old vs New Tax Regime Slabs Comparison for FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26)
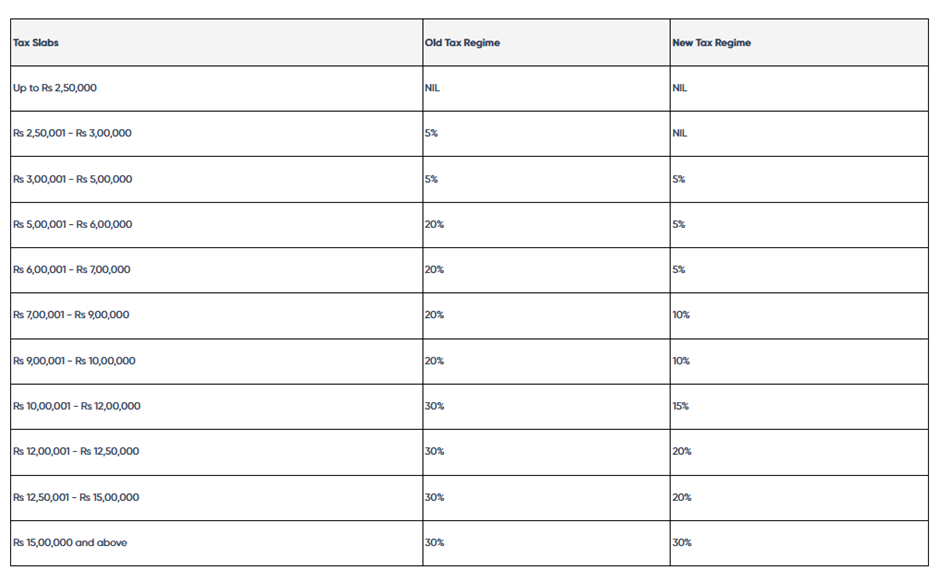
Major Deductions and Exemptions Not Claimable Under the New Tax Regime
Under the new tax regime, the following deductions and exemptions cannot be availed:
- Section 80TTA/80TTB: Deduction for interest on savings accounts or deposits for senior citizens.
- Professional Tax and Entertainment Allowance: Benefits available on salaries.
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): Tax-free travel reimbursement for employees.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): Exemption for rented accommodation.
- Allowances to MPs/MLAs: Special allowances for legislators.
- Minor Child Income Allowance: Exemption for minor children’s income.
- Helper Allowance: Allowance for employee assistants.
- Children Education Allowance: Tax relief on education expenses.
- Other Special Allowances [Section 10(14)]: Allowances granted to meet specific expenses.
- Additional Depreciation [Section 32(1)(iia)]: Extra depreciation for plant or machinery.
- Deductions under Sections 32AD, 33AB, and 33ABA: Related to specific investments and accounts.
- Deductions for Scientific Research [Section 35]: Donations or expenses under subsections (2AA), (1)(ii), (iia), or (iii).
- Deductions under Sections 35AD and 35CCC: Investment-linked incentives and agricultural extension projects.
- Housing Loan Interest [Section 24]: Deduction on self-occupied or vacant properties.
- Chapter VI-A Deductions: Includes Sections 80C, 80D, 80E, etc., except for Section 80CCD(2) (employer contribution to NPS) and Section 80JJAA (employment generation).
- Perquisites and Allowances: Exemptions for food allowances (₹50/meal, up to 2 meals/day) and other similar benefits.
- Employee’s Contribution to NPS: Personal contributions are not deductible.
- Donations to Political Parties or Trusts: Contributions under eligible sections.
These exclusions aim to simplify the tax structure while providing reduced tax rates under the new regime.
Exemptions and Deductions Available Under the New Tax Regime
The New Tax Regime offers select exemptions and deductions aimed at specific circumstances and benefits. Below is a summary of what you can claim:
- Transport Allowance: For specially-abled individuals.
- Conveyance Allowance: Received to cover conveyance expenses as part of employment.
- Travel Expenses: Compensation for travel on tours or transfers.
- Daily Allowance: To meet regular expenses incurred due to absence from the regular place of duty.
- Perquisites for Official Purposes: Tax-free benefits provided for official work.
- Voluntary Retirement Compensation [Section 10(10C)]: Exemption on amounts received on voluntary retirement.
- Gratuity [Section 10(10)]: Tax-free gratuity as per prescribed limits.
- Leave Encashment [Section 10(10AA)]: Exemption for leave encashment received by employees.
- Interest on Home Loan: Deduction under Section 24 for interest paid on a loan for let-out property.
- Gifts: Exemption for gifts received up to ₹50,000.
- Employer’s Contribution to NPS [Section 80CCD(2)]: Deduction for employer contributions up to 14% of salary (increased from 10% in Budget 2024).
- Additional Employee Cost [Section 80JJAA]: Deduction for employment generation.
- Standard Deduction:
- Introduced in Budget 2023: ₹50,000 (applicable from FY 2023-24).
- Increased in Budget 2024: ₹75,000 (applicable from FY 2024-25).
- Family Pension Deduction [Section 57(iia)]:
- Introduced in Budget 2023.
- Limit increased in Budget 2024 from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000.
- Agniveer Corpus Fund Contribution [Section 80CCH(2)]: Deduction for amounts paid or deposited.

RELATED POSTS
View all


